Automatic Test Case Generation
DescriptionSoftware Testing is one of the most important phases of the software development process. The objective of software testing is to find errors in the software and to assure its correctness with a high probability. An automatic test case generator is a tool that proposes a set of test cases to be run on a given program in order to check if the program satifies the functional or non-functional requirements. This problem has received much attention from the Search-Based Software Engineering (SBSE) community [1] and Evolutionary Algorithms have been the preferred optimization technique in this field of research. We can distinguish four large paradigms in search-based software testing that differ in the kind of information they use to generate the test cases and the final goal of the search: structural testing, functional testing (black box), grey-box testing, and non-functional testing. We focus here in structural testing, which has been the most popular. |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
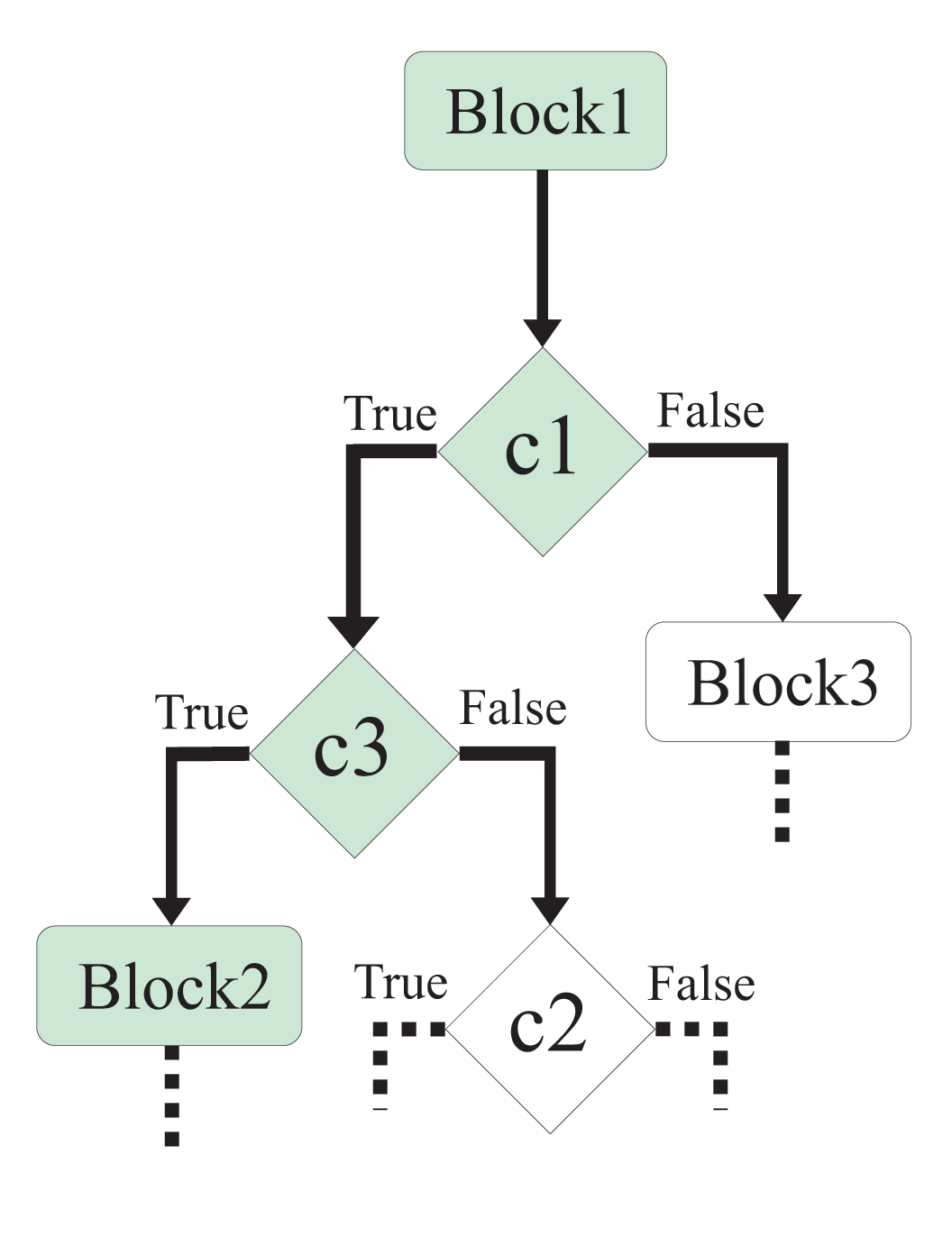
In structural testing the test case generator uses the structural information of the program to guide the search of new test cases (for this reason it is also called white-box testing). Usually, this structural information is gathered from the control flow graph of the program. The final goal of this search is to find a set of test cases that execute every testable element under consideration (statements, branches, conditions, etc.). In order to compare the quality of different test case sets a coverage measure is usually defined. This measure is the ratio between the number of testable elements (branches for example) executed by te test case set and the total number of testable elements in the program. There exist several coverage measures defined in the literature, some examples are: statement coverage, branch coverage, and condition coverage. Increasing the coverage and decreasing the number of test cases of a set are the two main objectives in this problem. The automatic test case generation is usually applied in the context of unit testing. In this case the element to test is a function with several parameters. A test case is a list of input values for the parameters of the function. The automatic test case generator breaks down the global objective into several partial objectives consisting of executing each particular testable element of the program. For example, if we use branch coverage we can identify six partial objectives in the fragment of the control flow graph shown above: to make branch
condition one true, to make branch condition one false, etc. Then, each partial objective can be treated as an optimization problem in which the function to
be minimized is a distance between the current input and an input satisfying
the partial objective. The way in which this distance is computed depends on the branch condition (for details see [2]). In order to solve such minimization problems, global search techniques like evolutionary algorithms can be used. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Test programsHere we publish the benchmark of test functions used in ref. [2]
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Related Bibliography and Papers
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

 26th Oct 2011.
26th Oct 2011. 


